Simon Coulthard October 29, 2024
8 Minute Read

According to Geoplugin research, 90% of marketers believe that geographic-based marketing drives more sales.
This makes geographic segmentation a powerful way to achieve better results.
If you're looking to explore the nuances of localized marketing, this blog is an excellent starting point. You'll learn about the geographic segmentation variables, see how marketers effectively implement them, and gain valuable tips for making it work for your business.
TL;DR
- Geographic segmentation is a marketing strategy that categorizes customers based on where they live in the world, allowing businesses to tailor products and services to meet local preferences and needs.
- The main variables considered in geographic segmentation are location (region, country, city, or neighborhood), time zone, cultural preferences, climate, and spending power.
- An example of a geographic segment could be marketing organic food products to health-conscious consumers in San Francisco’s Bay Area, where a large upper-class community has a strong demand for environmentally-friendly produce.
- Marketers can use website intelligence platforms like TWIPLA to collect the geographic segmentation data they need to guide strategies built around this model.
What is Geographic Segmentation?
→ The GPS of Market Demand
Understanding your customers is fundamental to business success, and their location is obviously one crucial aspect to consider.
This is where geographic market segmentation comes in.
Geographic segmentation is the process of dividing a market based on variables such as regions, countries, cities, or neighborhoods.
It’s one of the more obvious strategies for understanding consumer behavior, as location, cultural values, weather, and time zones all significantly influence preferences, purchasing habits, and other local trends.
Of course, companies can also segment their audience by demographic, behavior, and psychographics. And the fuzzy nature of these four main approaches to segmentation - and social theories more generally - means that they all overlap to some degree.
But analyzing geographic variables is a useful way for businesses to get deeper insight into their audience, which they can use to:
-> Enhance customer experience (CX) and satisfaction,
-> Improve brand loyalty,
-> And ultimately, drive sales.
This is particularly true in the modern digital age, with companies needing to find their geographic target market niche in an online space that is both global and local.
Given this, geographical marketing can act as a guiding principle, akin to a GPS system, that directs them towards profitable market opportunities.
How Do Marketers Use Geographic Segmentation?
“The primary reason to collect location data for 67% of marketers is for targeting”
Marketing is about showing the world your unique value.
But not everyone values the same thing.
Some audiences prefer rock stars, while others gravitate toward rappers, pop artists, or even poets — what resonates depends on who you're trying to reach.
Marketers use geographic segmentation to tailor their products and messaging to specific audiences, ensuring they meet local preferences and demands.
By thinking about geographic data when creating a marketing strategy, businesses can optimize strategies, messaging, and offerings to effectively engage their audience.
Here are a few ways they put this into practice:
- Localized Advertising: Marketers create geographic ads that resonate with regional interests, cultures, and language differences.
- Product Offerings: Brands often adjust their products based on geographic needs to better align with local preferences, cultural norms, and environmental conditions.
- Targeted Promotions: Global communities celebrate various events, and marketers frequently align their promotions with these local celebrations.
- Channel Optimization: People don’t all use the same platforms, so marketers leverage geographic segmentation to identify the most effective online and offline channels for reaching specific audiences.
- Pricing Strategies: Marketers may adjust pricing based on geographic factors, considering local economic conditions and consumer purchasing power to ensure their offerings are competitive and accessible.
This work allows businesses to offer the right products to the right audiences at the right price and time.
Put another way, it enables marketers to create meaningful connections with their audiences by taking local preferences, cultural nuances, and economic conditions into account.
Geographic insights are important when building user personas, and should be considered by CMOs in their planning.
As the market continues to evolve, the strategic use of geographic segmentation in marketing will remain a vital component of successful marketing campaigns.
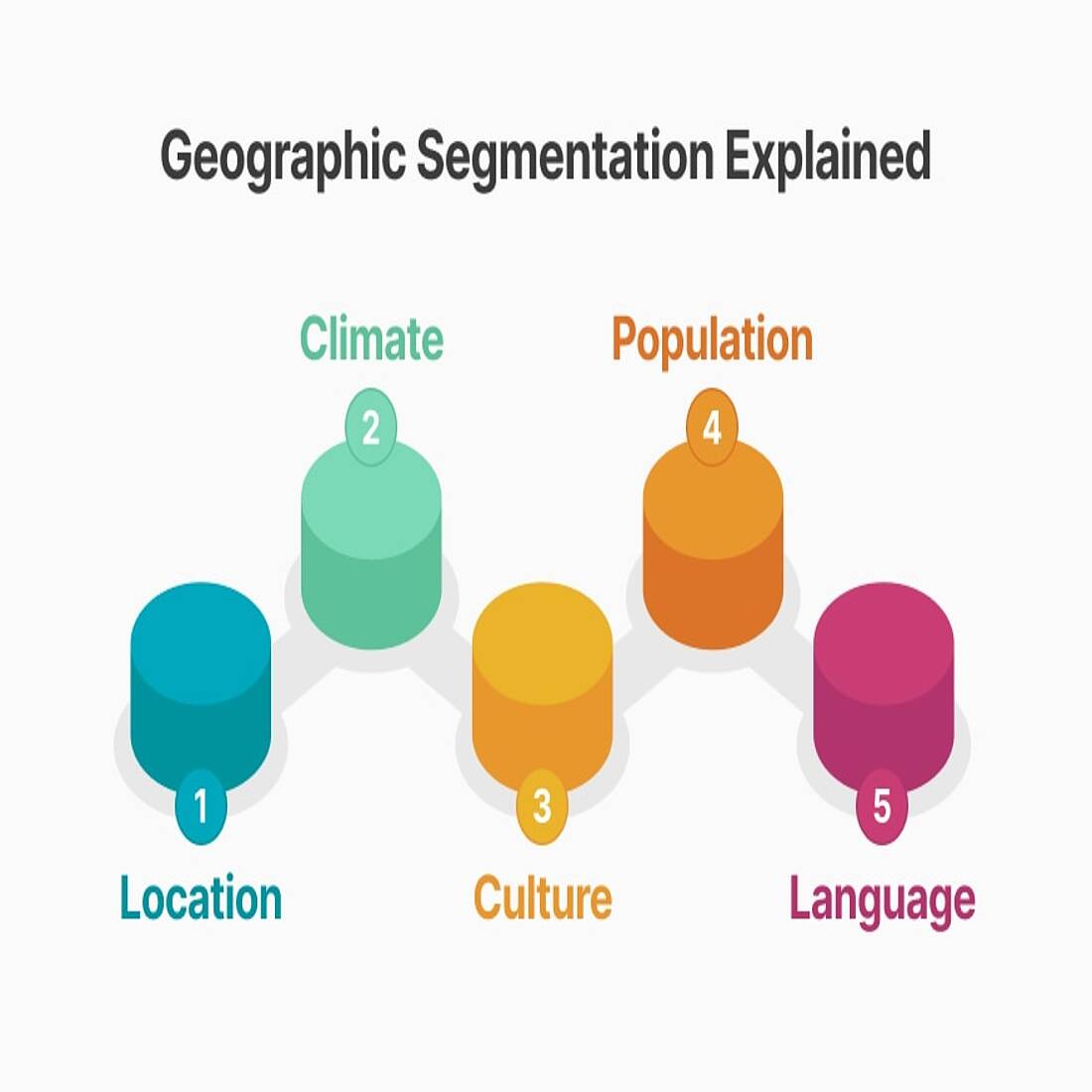
Key Geographic Segmentation Parameters
When using this approach, the main geographic factors or variables that marketers focus on include:
- Location: Dividing audiences by country, state, city, or even neighborhood.
- Climate: Understanding weather patterns to tailor products and services.
- Population Density: Urban, suburban, and rural areas have different needs and preferences.
- Cultural Preferences: Regional traditions or lifestyle differences can shape buying behavior.
- Language: Adapting marketing content to the dominant language spoken in each area.
At first glance, these geographic characteristics may seem obvious.
However, the challenge lies in knowing what to prioritize, where they tie together, and how to leverage this information effectively.
For instance, a business might discover that a significant portion of its audience is based in London. Yet, that insight alone is insufficient for crafting a targeted marketing strategy. London is a highly ethnically diverse city, and strategies that work in one district could fail completely in another.
To capitalize on geographic segmentation, marketers must dig deeper into the nuances of these parameters, gaining insights that inform more tailored and effective strategies.
Real-life Geographic Segmentation Examples
Geographic segmentation is crucial in sectors and industries heavily influenced by consumer behavior, such as food, travel, and retail. However, it’s beneficial for any business aiming to boost demand and sales.
By understanding the geographic nuances of their audiences, companies can tailor their offerings and marketing strategies more effectively.
Below, you’ll find some fascinating geographic segmentation examples of famous brands that are using this approach successfully:

McDonald's
The fast-food giant operates on the principle of menu standardization, enabling customers to know what to expect before entering any store.
However, they adapt their menus to meet local expectations, offering different items in each country.
For instance, McDonald's features the Teriyaki burger in Japan and the McArabia burger in Morocco, while avoiding beef burgers in India altogether to respect local dietary preferences and cultural beliefs.

Netflix
The streaming service tailors its content library based on geographic segmentation to better serve diverse audiences.
In different countries, Netflix offers varying shows and movies, often reflecting local cultures, languages, and viewing preferences.
For instance, popular series like Money Heist gained immense popularity in Spain, leading Netflix to invest in more original Spanish content. Similarly, in India, Netflix features a range of regional films and series, catering to diverse linguistic and cultural audiences, ensuring that their offerings resonate with local tastes and trends.
Nike
The sportswear giant employs geographic segmentation by customizing its marketing strategies and product offerings to align with local markets.
In regions with a strong emphasis on particular sports, such as soccer in Europe or basketball in the United States, Nike tailors its advertising campaigns and product launches accordingly.
Additionally, Nike often collaborates with local athletes and influencers to promote its brand, ensuring that the messaging resonates with the cultural values and preferences of the target audience.
This approach not only strengthens brand loyalty but also drives sales by creating a connection with consumers based on their unique sporting interests and lifestyles.
It might be better to include an image in this section that showcases all the brand logos together, making this part more visually appealing.

Ford
The automotive manufacturer leverages geographic segmentation to tailor its vehicle offerings and marketing strategies to diverse markets around the world.
In regions with varying environmental conditions and driving preferences, such as rugged terrain in Australia or snowy climates in Canada, Ford designs and promotes specific models that cater to those needs, like the Ford Ranger for off-road enthusiasts or the Ford Escape for urban dwellers.
Additionally, Ford’s marketing campaigns often reflect local culture and values, using regional language and imagery that resonate with consumers.
This localized approach not only enhances brand relevance but also ensures that Ford vehicles meet the specific demands of different markets, driving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Danish Crown
As one of Europe’s largest meat producers, Danish Crown utilizes geographic segmentation to optimize its product offerings across various markets.
The company tailors its product lines to align with local culinary traditions and consumer preferences.
For instance, in countries where pork is a dietary staple, Danish Crown emphasizes its range of pork products, while in regions where beef is more popular, it focuses on beef offerings.
Additionally, the company adapts its marketing strategies to reflect local customs and tastes, promoting specific cuts or products based on regional cooking habits.
By understanding the unique demands of each market, Danish Crown ensures its products resonate with consumers, enhancing both brand loyalty and market penetration.
These geographic segmentation marketing examples show just how powerful this approach can be. Tailoring products, marketing strategies, and content to align with regional preferences not only enhances customer engagement but also fosters brand loyalty.
As businesses continue to navigate a global marketplace, the ability to adapt and resonate with diverse audiences will remain a critical factor for success.
Making Geographic Segmentation Work for Your Product
To harness the power of geographic segmentation effectively, businesses must implement strategies that align with local market dynamics and consumer preferences. Here are several key steps to consider:
- Conduct Thorough Market Research: Start by analyzing geographic data to identify your target markets. This includes understanding demographic factors, consumer behavior, cultural trends, and economic conditions specific to each region. Utilize surveys, focus groups, and secondary data sources to gather insights that inform your segmentation strategy.
- Customize Product Offerings: Tailor your products to meet the unique needs and preferences of each market. This may involve altering features, sizes, flavors, or packaging based on regional tastes and cultural norms. Consider local customs and traditions to create offerings that resonate deeply with consumers.
- Localize Marketing Campaigns: Develop marketing messages and campaigns that reflect local culture, language, and values. Use region-specific imagery, terminology, and themes to make your brand relatable. Collaborating with local influencers or community leaders can also maximize your reach and website credibility.
- Leverage Distribution Channels: Optimize your distribution strategy based on geographic insights. Identify the most effective online channels and offline opportunities for each market, ensuring your products are readily accessible to consumers. Consider partnering with local distributors or retailers to enhance your market presence.
- Monitor Performance and Adapt: Continuously evaluate the performance of your geographic segmentation strategies. Use analytics tools like TWIPLA to track sales, customer feedback, and market trends. Be prepared to adapt your approach based on changing consumer preferences or emerging market opportunities.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can effectively leverage geographic segmentation to enhance product relevance, increase website engagement, and ultimately boost sales.
Understanding and catering to the unique characteristics of each market not only fosters brand loyalty but also positions companies for long-term success in a competitive landscape.
Use TWIPLA to Collect Geographic Data
Geographic segmentation is a vital consideration in modern marketing.
Thanks to TWIPLA, gaining location-based insights has never been easier.
Our comprehensive tools make data-driven decisions accessible to all businesses:
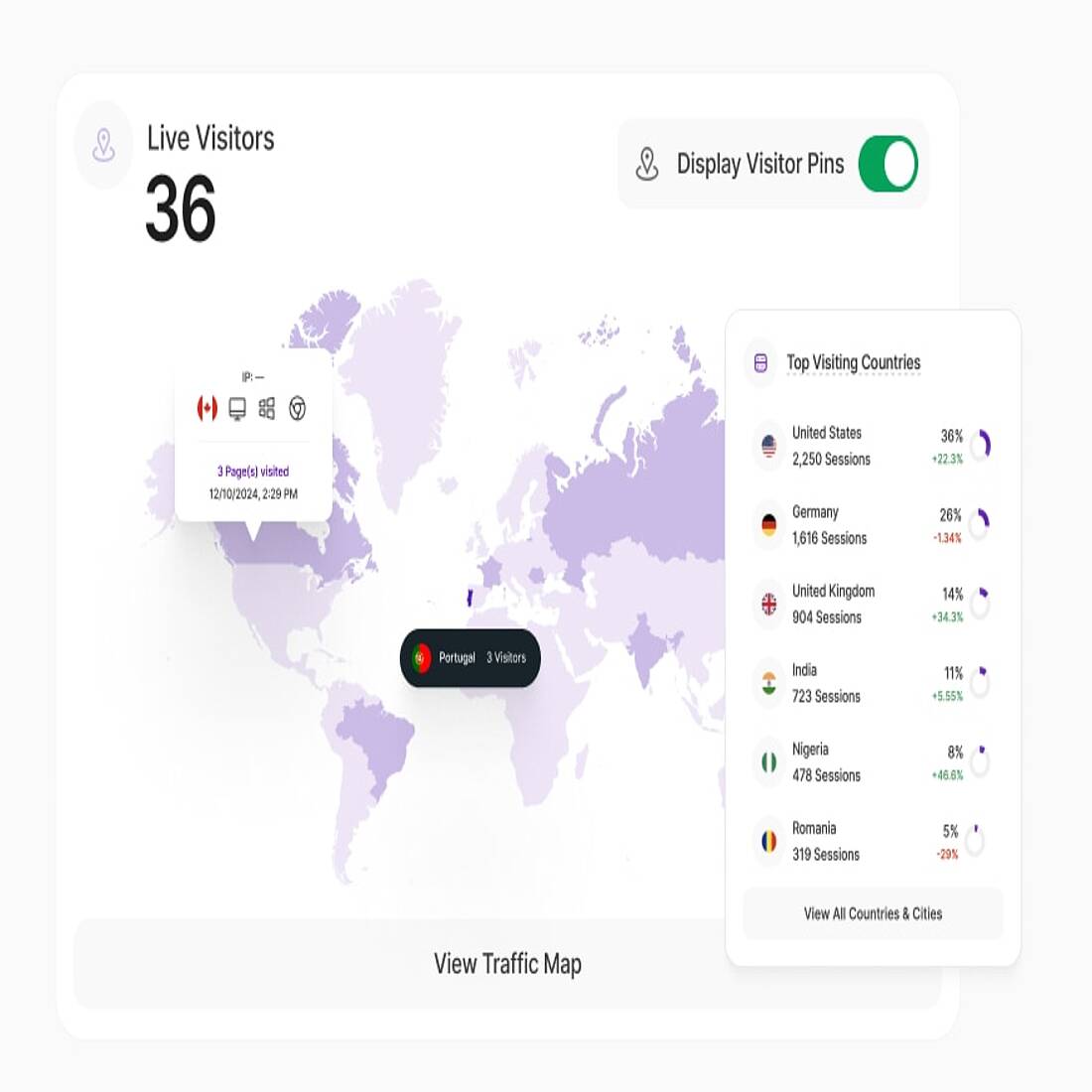
- All our website statistics and eCommerce modules can be filtered by location, allowing users to extract geographic data from website traffic. Additionally, a global map provides locations of site visitors right down to street level. These capabilities extend to UTM campaign analytics, offering insights into visitors’ countries of origin.
- The Visitor Segments feature and pre-set filter templates enable businesses to quickly access locational data, while custom dashboards provide cross-platform insights tailored to specific needs. This flexibility ensures you can generate the reports necessary to respond to evolving marketing dynamics.
- As a privacy-first website intelligence platform, TWIPLA allows businesses to set different privacy modes for any market. While our platform complies with all privacy laws by default, users can tailor privacy modes and compliance workloads based on the significance of specific markets and the depth of data they require.
By leveraging these features, businesses can fully harness geographic segmentation, enabling more precise targeting and ultimately driving higher engagement and conversions.
FAQs
What is Geographic Segmentation in Marketing?
Geographic segmentation is the practice of dividing a target audience based on their physical location, such as country, state, or city. This approach allows marketers to tailor their strategies and offerings to meet the specific needs and preferences of different regional markets.
Why is Geography Important in Marketing?
Geographics in business and marketing allow strategies to be tailored to local preferences, climate, culture, and purchasing behaviors, and to get better results from their output.
Where is Geographic Segmentation Most Useful?
Geographic segmentation is most useful in industries where location heavily influences consumer behavior, such as retail, travel, and food. However, any business can use it to increase efficiency by adjusting their operation to regional needs and conditions.
Share article
Get Started for Free
Gain World-Class Insights & Offer Innovative Privacy & Security

Stay Updated & Get Inbox Insights
Keep pace with the world of privacy-first analytics with a monthly round-up of news, advices and updates!
You might also like
Unlock the Power of Wix: 10 Must-Have Plugins for Your Site 23 May 2023 - by Simon Coulthard
23 May 2023 - by Simon Coulthard
16 Actionable Content Marketing Tips for Guaranteed Results 23 May 2023 - by Simon Coulthard
23 May 2023 - by Simon Coulthard