- Why Us?
- Features
White Label
For SaaS Platforms & Agencies
Provide our complete analytics suite to your clients, directly within your own interface and with your/their own branding. Discover Analytics-as-a-Service and White Label Analytics. Great benefit, minimal effort.
- Pricing
- White Label
- Success Stories
- ResourcesGetting Started
CONTENTS
- TL;DR
- Key Facts About Demographic Segmentation
- Demographic Segmentation Definition
- Demographic vs Other Segmentation Types
- Demographic Segmentation vs Targeting
- Real-life Demographic Segmentation Examples
- Segmenting by Age
- Segmenting by Sex/Gender
- Segmenting by Family Status
- Segmenting by Income
- Segmenting by Occupation
- Quick Demographic Segmentation Roadmap for Your Product
- FAQs for Demographic Segmentation
- What is Demographic Segmentation?
- What Characteristics Do Marketers Consider in Demographic Segmentation?
- What is a Demographic Segmentation Example?
Demographic Segmentation for Marketers: The Only Guide You Need

Demographic segmentation reveals the basic characteristics of your audience, and it’s the first step towards the personalization that’s at the heart of persuasive marketing.
Of course, selling products to the right people in the right place at the right time requires a little more depth. But without demographic data, you’re unlikely to hit the mark.
This blog will help you to understand demographics in marketing. In it, you’ll learn how to build this approach into a targeted marketing strategy, find examples of demographics in business, and get advice on how analytics fits into a segmentation roadmap.
TL;DR
- Demographic segmentation is a strategy that marketers use to divide their target audience into groups based on factors like age, gender, income, and education.
- These characteristics are important in shaping a person’s purchasing decisions, and marketing to specific demographics enables businesses to create more personalized and relevant campaigns that drive sales, conversions, and brand loyalty.
- One demographic segmentation example for a music streaming service could be middle-aged, high-income subscribers who are more likely to upgrade to a premium plan, prefer email over social media, and have a preference for 70s and 80s music.
- This data is easy to acquire. Demographic information can be pulled from government censuses, market research, or elsewhere. It can also be collected from your audience using TWIPLA, which enables businesses to survey their customers directly.
Key Facts About Demographic Segmentation
- Demographic segmentation can increase email open rates by 15% and drive three times more revenue compared to generic emails.
- Personalizing marketing campaigns around demographic data can lead to higher engagement rates and improved customer retention.
- Campaigns targeted using demographic information can improve conversion rates by up to 30%.
- Businesses that use demographic marketing will see an increase of up to 20% in ROI.
- Demographic segmentation helps businesses identify target markets more accurately, leading to better product development and specialized services.
Demographic Segmentation Definition
→ The Art of Knowing Who’s Who
Demographic market segmentation is the humanization of business.
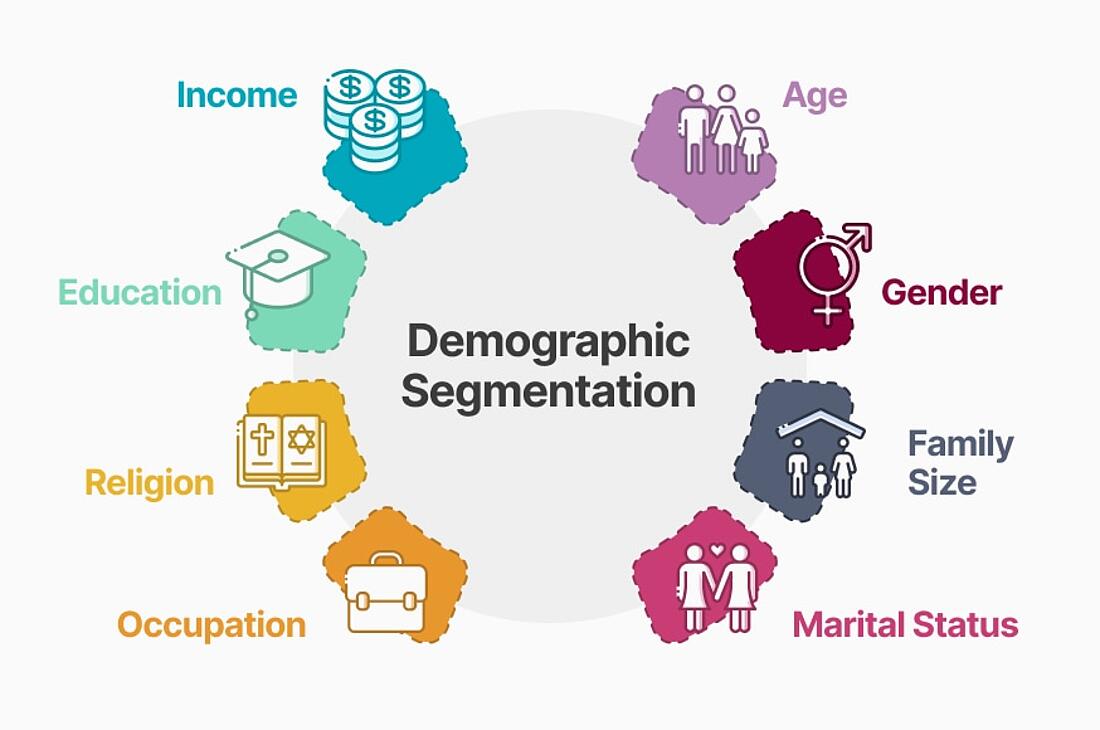
It’s a strategy that divides a target audience into distinct categories based on their defining characteristics:
Age, gender, family status, income, education, occupation, and so forth.
We may never really get to know the exact personalities of our customers, but demographic analysis allows us to get a rough idea.
It’s the art of knowing who’s who, peeling away the anonymity a little and seeing who's underneath.
By analyzing demographic categories, businesses can craft more personalized messages and create products that better align with the needs of each group.
Whether it's designing an ad campaign for younger, tech-savvy consumers or offering premium services to high-income earners, demographic segmentation helps marketers target their efforts more effectively.
Demographic audience segmentation is one of the most accessible and widely used forms of market segmentation due to its simplicity and the availability of data.
It’s an essential first step for businesses aiming to:
- Build targeted campaigns,
- Craft meaningful customer experiences, and ultimately,
- Boost sales and growth.
Of course, we live in the age of data privacy and it's important to build good consent management processes around personal data to meet legal requirements.
But knowing your customer base can still be done with respect for privacy, and it's the first step to reaching the right people at the right time with the right message.
Demographic vs Other Segmentation Types
While demographic segmentation is a valuable tool for understanding customer characteristics, it doesn't provide a complete picture.
For instance, age and gender give you some idea of your target audience, but no one believes that a 16-year-old tomboy and a fashionista of the same age will buy similar things from a clothing company.
Research into identical twins suggests that certain consumer preferences might be innate; however, these interchangeable individuals are rare, and everyone else has unique tastes and buying habits that demographic variables can’t predict completely.
Ultimately, demographic targeting is blind to the nuanced motivations and behaviors that drive consumer decisions.
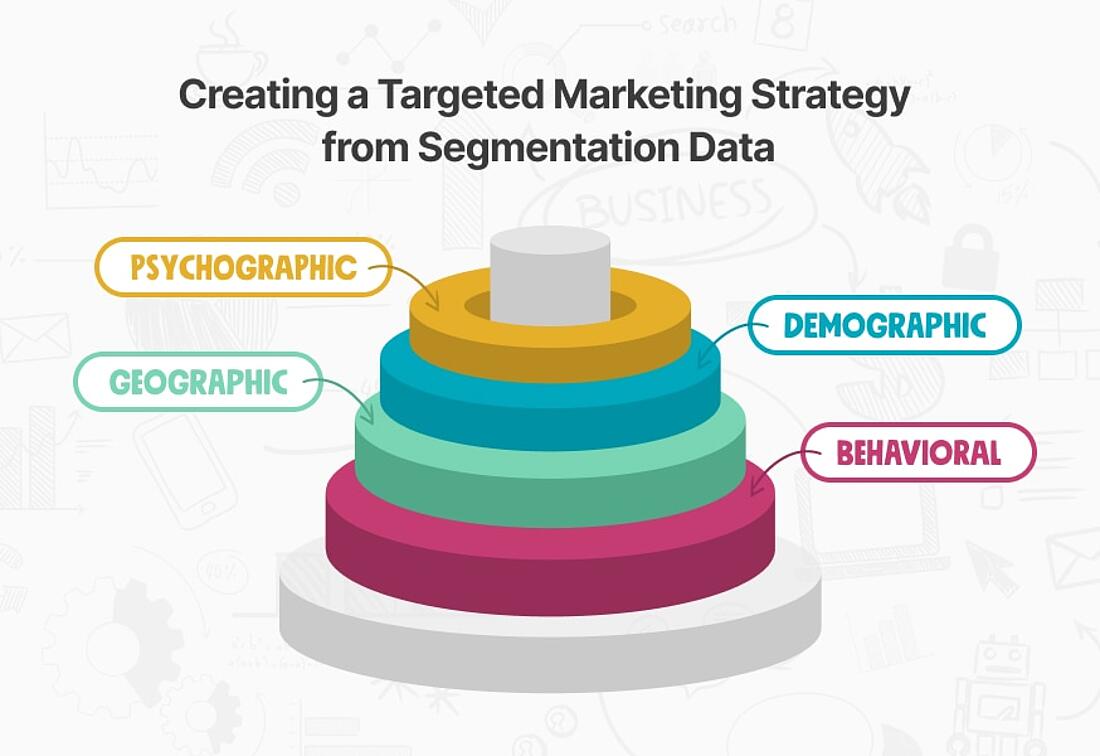
To develop more effective marketing strategies, businesses should consider integrating other segmentation methods into their audience research to gain a deeper understanding of their customers:
- Geographic Segmentation: This approach acknowledges that consumer preferences are often shaped by cultural factors related to their location, reflecting how regional influences can impact buying behavior.
- Psychographic Segmentation: This approach explores the lifestyles, values, and interests of consumers, categorizing them based on psychological traits and personality characteristics.
- Behavioral Segmentation: This approach focuses on how people interact with a brand, including their purchase history, browsing habits, and engagement patterns.
Demographic Segmentation vs Targeting
Demographic audience segmentation, like all the approaches covered earlier, is powerful enough for many businesses to base their marketing strategies on it alone.
For instance, it’s particularly suited to the education sector, where qualifications and age are key factors for institutions aiming to attract eligible students to their courses.
Similarly, demographic segmentation is effective in the real estate industry, as income, occupation, marital status, and family size significantly influence the property types that potential buyers or renters will find appealing.
However, by combining demographic segmentation with geographic, psychographic, and behavioral data, marketers can develop a much deeper understanding of their customers.
This is what is known as targeting.
It’s a multi-faceted approach that allows businesses to craft highly nuanced marketing strategies that resonate with the specific needs and preferences of their customers.
Hopefully, this helps to clarify the target demographic meaning and how it informs personalized campaigns.
It's also important not to confuse targeting with retargeting, as they are two different aspects of marketing.
Ultimately, leveraging all these segmentation options simultaneously can lead to more effective messaging, improved customer engagement, and higher conversion rates.
Targeting works like this:
After segmenting the market, a business must evaluate which categories are the most viable in terms of size, growth potential, and alignment with their products or services.
For example, if a shoe company discovers that they are most popular among people aged over 50, they might decide to target this group with campaigns that highlight the comfort, stability, and style of their footwear, crafting messages that address the specific needs, preferences, and language that strike a chord with older consumers.
However, effective targeting means integrating geographic, psychographic, and behavioral factors.
This means that they might:
- Analyze where this demographic lives as a basis for regional campaigns.
- Research their lifestyle choices to better appeal to these consumers.
- Assess buying habits and use this data to inform the finer points of their strategy.
So while customer demographic segmentation provides a good jumping off point for audience selection, targeting translates these insights into the type of focused strategy that will best drive engagement and sales.
By leveraging all their segmentation data, businesses can create more meaningful connections with their audiences and achieve better marketing outcomes.
Real-life Demographic Segmentation Examples
Demographic segmentation is a widely used approach in marketing that helps businesses build strategies that align with specific audience segments.
Below are real-life demographic factor examples, showing how famous companies effectively segment their audiences based on these key characteristics:
Segmenting by Age

Many companies use age as a primary demographic variable when designing products and marketing strategies.
For instance, Disney know their user personas: the young or young-at-heart, and they create content and experiences that cater to these age groups. Their films, theme parks, and merchandise are designed primarily with children in mind, but they also appeal to the inner child of nostalgic adults who grew up with Mickey Mouse and friends.
While their entertainment may sometimes lack the bite that many adults seek from certain intellectual properties, this approach allows Disney to develop targeted marketing campaigns that captivate both children and adults, ensuring they engage the broad audience necessary for their success.
Segmenting by Sex/Gender

Procter & Gamble is one of the world’s largest consumer goods companies and has successfully leveraged gender-based segmentation in its marketing strategies.
For example, their brand Always focuses on women’s menstrual health and hygiene, crafting campaigns that empower women and address specific concerns related to menstruation.
Conversely, products like Gillette target men with messages centered around masculinity and grooming.
However, modern identity politics has introduced complexities that can challenge the reliability of this traditional approach.
Despite these evolving dynamics, Procter & Gamble effectively develops its marketing messages and product lines by understanding the diverse needs and preferences of each gender, ensuring they connect with their target audience.
Segmenting by Family Status

Family status segmentation is an effective way for businesses to identify consumers based on what is a key characteristic of their lifestyle.
For instance, baby product companies like Johnson’s Baby specifically target new parents, emphasizing safety, comfort, and the bonding experiences that are crucial for those navigating the challenges of parenthood. Their marketing campaigns connect with new parents by addressing their concerns and needs.
Similarly, Kraft Foods positions its products to appeal to families by promoting quick and easy meal solutions for busy households. When advertising to demographic groups, they often highlight family bonding during mealtime, positioning their products as a way to bring families together.
Interestingly, many cereal boxes feature characters looking down from supermarket shelves, designed to catch the attention of children. This strategy aims to persuade kids to urge their parents to buy the products.
Ultimately, this segmentation based on family composition allows companies to address the unique needs of the household types they are targeting, creating marketing strategies that appeal to their audience.
Segmenting by Income

Income segmentation allows businesses to target consumers based on purchasing power.
Luxury brands like Gucci and Louis Vuitton tailor their marketing to high-income individuals, emphasizing exclusivity, prestige, and high-quality craftsmanship in their campaigns.
In contrast, companies like Walmart focus on budget-conscious consumers, highlighting affordability and value.
By segmenting their audience by income, these brands can effectively position their products and services to meet the expectations of their target market demographics.
Segmenting by Occupation

Occupational segmentation gives businesses the capability to fine tune their marketing to the professions of their target audience.
For example, office supply companies such as Staples and Office Depot focus their marketing efforts on professionals in corporate settings. Their campaigns emphasize productivity, efficiency, and the latest office technology to appeal to this demographic.
On the other hand, brands like Carhartt target blue-collar workers by offering durable clothing suited for manual labor - even if their appeal also extends to skaters and other more fashion-focused consumers.
Still, they’re hugely successful because they understand the specific needs and preferences associated with different occupations.
Quick Demographic Segmentation Roadmap for Your Product
Creating an effective demographic segmentation strategy is a fairly straightforward process.
Here’s a roadmap to guide your efforts:
- Define Your Objectives: Start by clearly outlining your marketing goals. What do you hope to achieve through demographic segmentation? Whether it’s increasing brand awareness, boosting sales, or launching a new product, having defined objectives will shape your approach.
- Identify Key Demographic Variables: Consider which demographic characteristics are most relevant to your product. Common variables include age, gender, family status, income, and occupation. Prioritize these factors based on your target market and product type.
- Collect Demographic Data: Utilize tools like TWIPLA's website intelligence platform to gather essential demographic data. With communication modules such as surveys and polls, you can easily collect insights directly from your audience. Write questions in a way that will uncover specific demographic information that aligns with your segmentation goals.
- Analyze the Data: Once you’ve collected the data, analyze it to identify patterns and trends. Look for common characteristics within your audience that can inform your marketing strategies. This analysis can help you understand the unique needs and preferences of each segment.
- Segment Your Audience: Based on your analysis, create distinct demographic segments. Group your audience according to shared characteristics, ensuring each segment reflects a specific aspect of your target market.
- Develop Targeted Marketing Strategies: Craft tailored marketing campaigns for each demographic segment. Utilize insights gathered from your data to ensure your messaging resonates with the unique preferences and needs of each group. Consider various communication channels to effectively reach your audience.
- Monitor and Adjust: After launching your campaigns, continuously monitor their performance using analytics tools. Gather feedback and assess how well your segmentation strategies are working. Be prepared to adjust your approach based on the data and feedback you receive, allowing for ongoing optimization.
By following this roadmap and leveraging TWIPLA's tools, you can effectively use marketing demographics to enhance your business strategies. This approach not only enables you to better understand your audience but also empowers you to create meaningful connections that drive engagement and conversions.
FAQs for Demographic Segmentation
What is Demographic Segmentation?
Demographic segmentation is defined as the process of dividing a business’ target market, audience, or customers into groups based on variables like age, gender, and occupation.
What Characteristics Do Marketers Consider in Demographic Segmentation?
Marketers analyze core characteristics like age, sex, and marital status, but also consider factors like life stage and culture. These help them tailor messages that resonate with target groups, with the hope of increasing personalization and campaign success.
What is a Demographic Segmentation Example?
A luxury electric car company might target middle-aged professionals with high incomes that value sustainability and status from their peers. Alternatively, a fast-food chain could target busy families that want convenience, value, and a child-friendly environment.
Share article
Get Started for Free
Gain World-Class Insights & Offer Innovative Privacy & Security

You might also like
Interview: Orbit Media CEO Andy Crestodina 20 September 2024 - by TWIPLA Staff
20 September 2024 - by TWIPLA Staff
What Is A Data Breach? Definition, Types, Examples 11 September 2024 - by Simon Coulthard
11 September 2024 - by Simon Coulthard
Data Privacy vs. Data Security: Can They Coexist? 27 August 2024 - by Simon Coulthard
27 August 2024 - by Simon Coulthard