- Why Us?
- Features
White Label
For SaaS Platforms & Agencies
Provide our complete analytics suite to your clients, directly within your own interface and with your/their own branding. Discover Analytics-as-a-Service and White Label Analytics. Great benefit, minimal effort.
- Pricing
- White Label
- Success Stories
- ResourcesGetting Started
CONTENTS
- Let's start with the ABC definitions of data privacy vs security
- What is Data Privacy?
- What is Data Security?
- The Privacy-Security Paradox
- Data Privacy vs Data Security vs Data Protection
- Personal Perspective
- Business Perspective
- The Tug of War → What Should You Prioritize?
- FAQs for Data Privacy and Security
- What is the difference between privacy and security?
- What is an example of data privacy and data security?
- What is more important, data privacy or security?
- Is Privacy Possible Without Security?
Data Privacy vs. Data Security: Can They Coexist?

“Data is the pollution problem of the information age, and protecting privacy is the environmental challenge”
That’s a quote from Bruce Schneier, an IT security professional and privacy specialist. He's also a prolific writer, and you can read his work on Schneier's personal website.
He's got a way with words and this quote is a nice analogy that captures just how important good personal data management is in the online world.
Just as pollution poses significant challenges to our environment, data security and data privacy are vital concerns in the information age.
Understanding and addressing these issues is crucial to protecting customer data rights and helping to build the safe, trustworthy digital environment that we all want.
This blog is a great place to start grasping the basics of data privacy and security.
In it, you'll learn what these two concepts are, how they knot together to form the privacy-security paradox, and how they feed into the wider field of data protection.
It also includes practical tips for how businesses can start building better privacy and security measures.
Let's start with the ABC definitions of data privacy vs security
Data privacy is about Access: who can access personal information, how it’s collected, used, and shared, ensuring it aligns with user consent and privacy laws.
Data security is about Barriers: implementing protective measures like encryption, firewalls, and secure access controls to shield data from unauthorized access and breaches. While privacy focuses on the ethical handling of personal data, security emphasizes the technical safeguards needed to protect it.
Together, they form the Core of a comprehensive data protection strategy, ensuring both the ethical management and safety of sensitive information.
Balancing both is essential for building trust and maintaining compliance in the digital age.
But if you want to learn more, keep reading!
What is Data Privacy?
Data privacy is about protecting personal information and empowering internet users with agency over their data.
It covers the systems and processes that work to ensure that data is collected, used, stored, and shared only with the consent of the person it belongs to.
Data privacy is crucial because it helps protect individuals from unauthorized access and misuse of their personal information, which can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and other harms.
It also fosters trust between users and organizations, ensuring that data practices are transparent and respectful of individual rights.
If you remember the Ashley Maddison data breach, you'll understand just how serious data privacy violations can be.
Back in 2015, an anonymous group stole and released thousands of profiles from the site and released them online. Ashley Maddison was a dating site for people looking to cheat on their partners. It was hardly a morally virtuous endeavour, but the fallout was huge:
Victims had their reputations destroyed and suffered extortion on a massive scale. Some took their own lives as a result. Others filed a $567 million class-action lawsuit against the company, and there's even a fascinating docuseries on Netflix if you want to learn more about what was, at it's heart, a frightening data privacy scandal for everyone involved.
Imagine that you're using an online storage service to organize your photos and documents. Data privacy means that only you and other people you've selected can access these files, and the provider doesn't use them for its own purposes.
Website Example: Data privacy is the cookie banner that appears when users visit a website, asking them to consent to the use of cookies. Visitors can accept or decline non-essential cookies based on their comfort level with sharing personal information.
Other examples that mesh with the data privacy definition include:
- Privacy Policies: A well-written website privacy policy providing clear, accessible explanations of how the business collects, uses, and protects personal data.
- Opt-Out Options: Allowing users to opt out of certain data collection practices or marketing communications.
- Data Access Rights: Giving individuals the ability to access, correct, or delete their personal data upon request.
- Data Minimization: Collecting and retaining only the minimum amount of personal information necessary for a specific purpose, reducing the risk of misuse and enhancing privacy protection by limiting data exposure.
Data privacy is governed by various regulations globally, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States.
These are just two of the hundreds of data privacy laws that have mushroomed around the world in recent years.
They set standards for data handling and help ensure that personal information is managed with the utmost respect and care.
What is Data Security?
Data security is about protecting information from unauthorized access, breaches, or theft.
For businesses, the benefits are clear. Data security provides protection from data breaches and cyberattacks, which helps avoid financial losses and reputation damage.
It also ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of fines and legal action.
Think back to that online storage service that was mentioned earlier. These files are personal, and you wouldn't want hackers to be able to easily get inside and steal your photos and documents - data security is there to stop this from happening!
And to prevent any unauthorized access, the storage service implements data security measures.
This includes using encryption, which applies special codes to your files so that only you can unlock and view them.
They also secure access to your account by requiring strong passwords and additional security checks, ensuring that no one else can access, steal, or tamper with your files.
Website Example: In the context of a cookie banner, data security involves encrypting the personal data collected and stored by cookies. This ensures that, even if someone tries to access this information without authorization, they would be unable to read or misuse it.
Secure data storage is obviously key, but this is ultimately an umbrella concept for a range of other aspects that fit the data security definition, including:
- Access Controls: Implementing measures such as passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls to limit who can view or modify data.
- Firewalls and Antivirus Software: Using these tools to protect systems from malicious attacks and unauthorized access attempts.
- Data Anonymization and Pseudonymization: Implementing encryption techniques to protect sensitive personal information, either by fully anonymizing data to prevent re-identification or by using pseudonyms to reduce exposure while allowing limited linkage under controlled conditions.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Regularly backing up data and having recovery plans in place to restore information in case of data loss or corruption.
- Security Audits: Conducting periodic reviews and tests to identify vulnerabilities and ensure that security measures are effective.
Data security practices are guided by various standards and frameworks, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 27001 and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework.
These guidelines help organizations implement robust security measures and protect sensitive information effectively.
The Privacy-Security Paradox
→ Can One Exist Without the Other?
In many ways, these concepts are two sides of the same coin.
Data privacy and data security are intertwined, creating a complex relationship known as the privacy-security paradox.
→ There’s no data security without privacy since data could be misused or shared without the person’s consent
→ There’s no data privacy without security since data could easily be exploited or misused regardless of what the person has consented to.
As you can see, privacy and security complement each other.
Strong data security measures ensure that personal information remains safe from external threats, while effective privacy practices ensure that individuals have control over their data.
One cannot effectively exist without the other - good security practices enhance privacy by keeping data safe, while strong privacy policies build trust and foster responsible data handling.
Website Example: A business might implement rigorous encryption to protect user information, but without clear privacy policies and user consent mechanisms, even the most secure systems could fall short in ensuring users’ trust and compliance with legal standards.
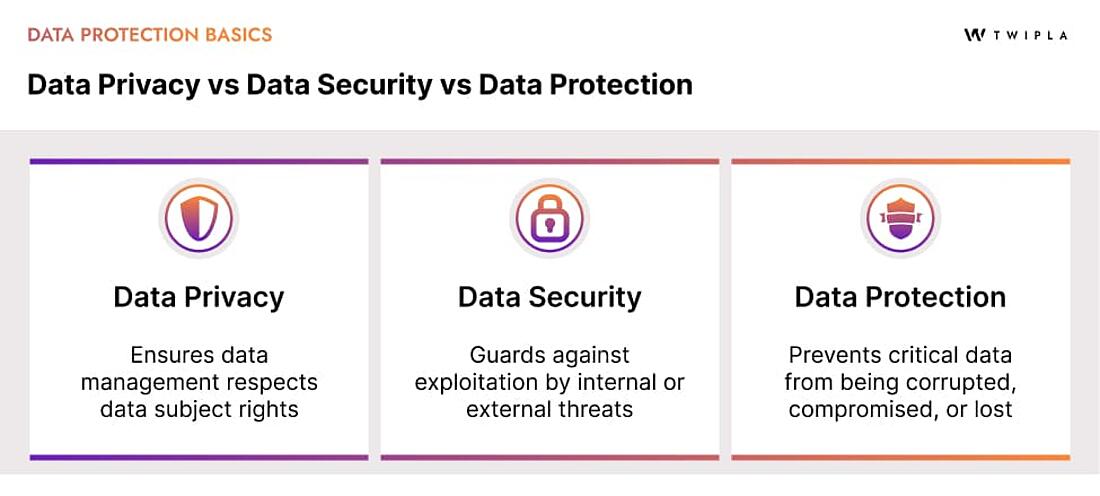
Data Privacy vs Data Security vs Data Protection
Now that you grasp the delicate interplay of data security vs data privacy, it’s important to understand how these elements contribute to the broader concept of data protection.
Data protection encompasses the practices and policies designed to safeguard data from unauthorized access and misuse while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
It’s an integrated approach that includes both data privacy and data security.
In practice, data protection involves creating a comprehensive framework that incorporates preventive, detective, and corrective measures to manage and secure data throughout its lifecycle.
For example, a robust data protection strategy might include:
- Encrypting data to ensure it remains secure from unauthorized access (security).
- Obtaining consent from individuals before using their data to respect their privacy rights (privacy).
- Regularly auditing and updating policies to ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR and to address emerging threats (data protection).
Below, you'll find handy tables that summarize the differences between data privacy, data security, and data protection from the perspective of individuals and businesses respectively:
Personal Perspective
Data Privacy | Data Security | Data Protection | |
Focus | Protecting personal information and keeping it private. | Ensuring your data remains secure from threats. | Implementing practices to prevent data misuse. |
Example 1 | Controlling who can see your social media profile. | Using strong passwords and two-factor authentication. | Ensuring your personal data isn’t shared without consent. |
Example 2 | Choosing not to share location data with apps. | Enabling two-factor authentication on your accounts. | Backing up important personal documents to an external hard drive. |
Business Perspective
Data Privacy | Data Security | Data Protection | |
Focus | Compliance with regulations like GDPR. | Preventing unauthorized access to data. | Minimizing risks of data breaches and ensuring proper data handling. |
Example 1 | Implementing a consent management platform for user data collection. | Adding firewalls, encryption, and access controls. | Regularly backing up business data to secure, off-site locations. |
Example 2 | Creating and enforcing a company-wide data privacy policy. | Conducting regular audits to identify threats. | Encrypting emails to protect confidential information. |
By integrating these elements, organizations can create a well-rounded approach to data protection that not only defends against security threats but also respects and upholds individual privacy rights.
Data management involves a lot of spinning plates, and businesses can often face challenging decisions about where to focus their attention.
Data privacy and data security are both important, but determining which aspect should take precedence depends on a range of factors, including the nature of the data itself, the regulatory requirements that impact the business, and the specific risks they face.
Businesses can best work to balance their priorities by considering the following:
Firstly, understand your data.
Start by evaluating the types of data you handle.
Personal and sensitive information, such as financial records or health data, often require stronger privacy measures due to their inherent sensitivity and it’s particularly important to ensure that this data is collected, used, and shared with consent.
Next, understand your legal requirements.
Which data privacy regulations impact your business, or protect the data it collects?
And to be sure, speak to your lawyers.
Different data privacy laws set different obligations, making it important to understand the legal landscape that you’re working with and to align your priorities accordingly.
Thirdly, carry out a risk assessment.
What dangers lurk in the shadows around your data?
To find out, conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify any potential vulnerabilities.
And if you find that the main threat to your data is from cyberattacks and breaches, then enhancing security measures might be your immediate focus.
Conversely, if this main threat is actually from data being mishandled or shared without authorization, then strengthening privacy measures may take precedence.
Here are some other practical tips for balancing your priorities:
- Implement Comprehensive Policies: Develop and maintain policies that address both privacy and security. This integrated approach will help you manage data more effectively and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits to assess the effectiveness of your privacy and security measures. This helps identify any gaps or areas for improvement, ensuring that both aspects are adequately addressed.
- Education and Awareness: Use data privacy training to instill in staff the importance of both data privacy and security. Ensuring that your team understands their role in protecting data can enhance overall effectiveness and compliance.
But remember, prioritizing privacy over security or vice versa isn’t strictly necessary.
Instead you could focus on creating a balanced approach that integrates both aspects into your overall data protection strategy.
And by understanding your data, complying with regulations, and addressing risks before anything bad happens, you can effectively manage and safeguard personal data while maintaining customer trust and data utility.
FAQs for Data Privacy and Security
What is the difference between privacy and security?
The difference between data privacy and data security is clear, even if it’s hard to separate them in a practical sense. Privacy refers to the rights and practices related to the handling of personal information. Security, on the other hand, pertains to the measures and technologies used to protect data from unauthorized access, breaches, and theft. It involves safeguarding data through encryption, firewalls, and other protective mechanisms to prevent it from being compromised by external or internal threats.
What is an example of data privacy and data security?
Data Privacy Example: A company’s website displays a cookie consent banner that informs users about the types of cookies being used and requests their permission before tracking their browsing behavior. This ensures that users have control over how their data is collected and used. Data Security Example: An organization encrypts sensitive customer information stored in its database to protect it from unauthorized access. Even if a hacker gains access to the database, the encrypted data remains unreadable and secure.
What is more important, data privacy or security?
Both privacy and security are crucial but their importance varies depending on the context. Security is fundamental for protecting information from breaches and theft. Privacy is essential for respecting and managing individuals' rights to control their own information and ensuring ethical use. In practice, a balanced approach is necessary. Effective data protection relies on both strong security measures to safeguard data and robust privacy policies to manage how data is collected and used. Prioritizing one over the other can lead to vulnerabilities and potential non-compliance with regulations.
Is Privacy Possible Without Security?
Privacy is not fully achievable without security. While privacy focuses on how data is managed and who has access to it, security ensures that this data is protected from unauthorized access and breaches. Without security measures in place, even the best privacy practices can be compromised. Therefore, effective data privacy relies on robust security to ensure that personal information is both protected and managed responsibly.
That's Data Privacy and Security Explained!
Having read this blog, you hopefully have a better idea of what is privacy and security.
Of course, this is just an introduction and there's more to learn if you want to get your business compliant with data privacy legislation and secure from data threats.
But we're data privacy experts here at TWIPLA so be sure to check out our blogs and other resources when you want to dig deeper into the subject.
And if you want to be updated about any new content we publish, sign up to our newsletter. That way, you'll receive an email near the end of each month to links to all our new marketing insights, as well as information on product updates and other in-house activity.
Share article
Get Started for Free
Gain World-Class Insights & Offer Innovative Privacy & Security

You might also like
Data Anonymization vs Pseudonymization 12 July 2024 - by Simon Coulthard
12 July 2024 - by Simon Coulthard