- Why Us?
- Features
White Label
For SaaS Platforms & Agencies
Provide our complete analytics suite to your clients, directly within your own interface and with your/their own branding. Discover Analytics-as-a-Service and White Label Analytics. Great benefit, minimal effort.
- Pricing
- White Label
- Blog
- Chatbots, Assistants & AI Search: Tracking AI-Driven Website Traffic
- Use Case: Using TWIPLA’s Conversion Funnels to Uncover Onboarding Friction
- Website Intelligence News Roundup February 2025
- Website Intelligence News Roundup January 2025
- Alarming Behavior Tracking: Dead Clicks, Rage Clicks and More
- Data Management Strategy: Steps + Insights from Aleksejs Plotnikovs
- Craft a Successful Data Analytics Strategy in 6 Steps
- Interview: Aaron Weller on AI Privacy Challenges
- ResourcesExpand Your KnowledgeGetting Started
Sleep Tight, Data Safe: Secure Data Storage Guide

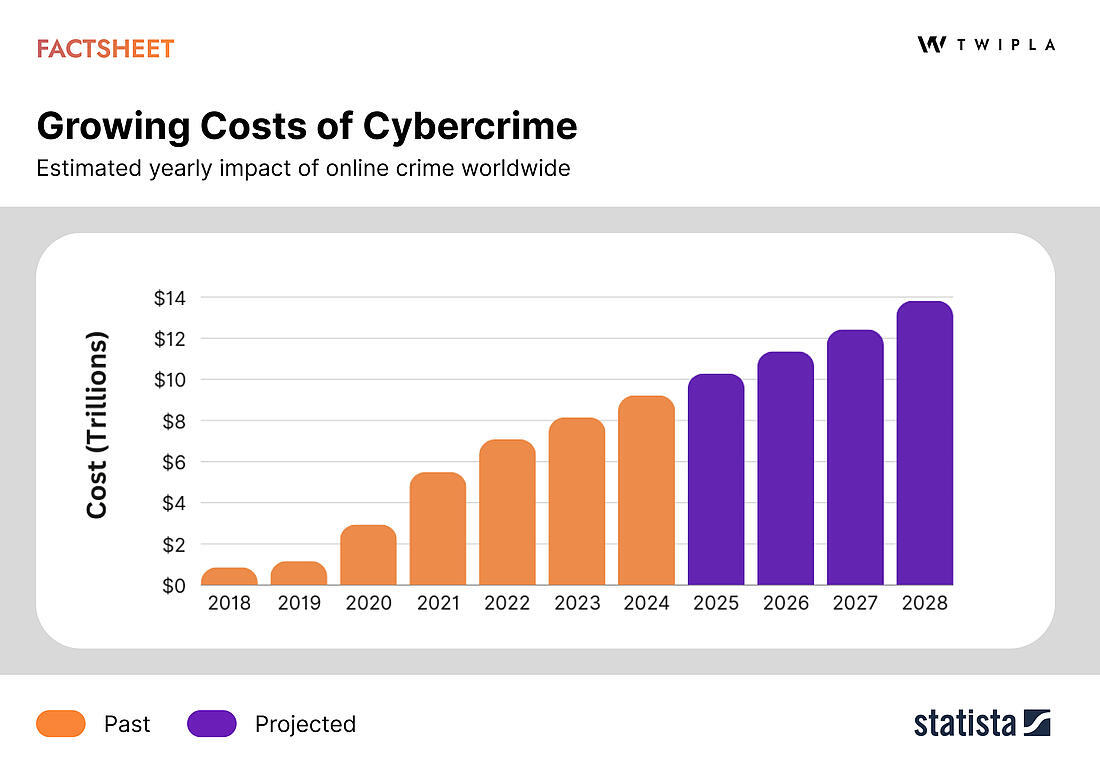
Did you know that cybercrime costs the global economy $9.22 trillion annually? And looking forward, Statista research estimates that this figure will grow to $13.82 trillion by 2028.
It’s certainly a worry for businesses, who can mitigate risk by implementing secure data storage. But such infrastructure is also an essential requirement under privacy compliance legislation, and good storage habits will reduce operating costs in the long run and increase credibility in the eyes of clients, customers, and other stakeholders.
In this blog, you’ll learn more about the importance of secure data storage for businesses. It also outlines the strengths and weaknesses of different data storage types, and the features that characterize the most secure data storage solutions.
Let’s dive in!
Our Critical Need for Secure Data Storage
Data’s the most valuable resource in the world. That’s from The Economist back in 2017. It’s a bold claim but they did the math. And if it was true then, it’s even truer today. We’re living in the age of Big Data and it’s no exaggeration to say that this information is the most prized commodity in the modern business world.
Unfortunately, digital data is also the most vulnerable of resources. It’s intangible and can be lost or corrupted easily. Human error can damage or block access. Hackers can also steal it to sell onlline, making personal data and the dark web uncomfortable bedfellows.
It's striking that cybercrime is growing so fast, and particularly since the internet has been such a central part of life for so long. Experts put this down to factors such as exploding global access to the digital space, the growing prevalence of remote working, automation, and the amount of personal data accessbile on the web via cloud storage services.
And unfortunately, every business is a target for online crime because they all have assets - financial, personal information, or otherwise - that criminals can exploit. According to Verizon, 43% of cyberattacks target small businesses, and an estimated 60% succumb to their wounds and shut down within six months of an attack.
This risk can be reduced significantly by securing data properly. In fact, IBM estimates that the yearly impact of poor data storage practices costs US businesses $3.1 trillion.
That’s quite the figure, and it underlines the importance of data storage security for the huge amount of personal and corporate data that businesses hold on their employees, customers, and others. In the past, most of this would have been printed and stored in top-heavy filing cabinets but it’s mostly digitized today and needs to be stored and managed safely.
And with digital data, this means adopting an infrastructure that ensures “CIA”, an acronym for the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
CIA is a great guide to data protection, and helps businesses to identify what attackers may target, and to then impliment preemptive countermeasures that adequately protect them.
Ultimately, such secure data storage ensures that this vital company resource is safe from theft, corruption, and other damage. It means that businesses can control who has access to it, and can share it easily with others when necessary. It also helps businesses to be able to find the information they need, when they need it. And it makes economic sense, saving time and money. Simply put, it’s a key building block of success.
However, businesses also have a legal responsibility to look after any data on file and to ensure that the risk of misuse or theft is kept to a minimum. Take GDPR, the EU’s data privacy law and the pacemaker for many similar regulations that came after it. This law sets expectations for a business’ data storage practices and those that don’t risk huge fines and real damage to their reputations.
But even away from the glare of enforcement agencies, consumers care about their data and expect it to be stored properly. Businesses known for poor data storage protection will shed customers, who will migrate to competitors with a better data governance reputation.
As such, secure data storage is great for website credibility. It's great for a business' wider reputation and brand image. It feeds into important metrics like customer aquisition and retention costs. And it can also help boost the ESG rating that qualifies companies for sustainability investment assets.
Key Types of Data Storage to Protect Sensitive Information
Data storage can be done on-prem, on the cloud, or through a hybrid combination of the two. But it’s important to note that, regardless of the option, the data itself is stored on physical hardware somewhere - a fact that many can overlook.
The difference between these approaches is ultimately ultimately down to the location of the data storage system, your level of accessibility to the hardware, and the various cost models involved. And each of these options can also provide the necessary security that businesses need for their data.
Let’s have a look at the different options:
Physical Data Storage Solutions

Physical data storage refers to hardware that businesses can touch in-house and is also known as on-prem or local storage. Put another way, it refers to the servers or other storage devices that businesses control and operate themselves. It also represents the structure of a database, and defines how data is stored, organized and accessed.
Servers are obviously the most common option that work to integrate a company’s IT network together, but high capacity data storage options have become much smaller in recent years.
Today, and depending on their size, businesses can also use hard disks, solid state drives, network attached storage, storage area networks, optical storage, and even flash disks and memory cards. Physical storage has its drawbacks: devices can fail, become incompatible (e.g., a hard drive not readable on Mac), be lost or stolen. But when done right, it's probably still the most secure data storage option because more sensitive information can be kept away from the web.
Advantages of Physical Data Storage for Businesses
- Ease of Accessibility: Since these devices are normally stored on-site, they’re easy to access - even without an internet connection.
- Portability and Sharing: Some physical devices can be carried anywhere, enhancing ease of accessibility even further.
- Faster Speed: Physically storage is generally faster than alternatives, and also streamlines backup work and recovery operations.
- Control and Security: Physical storage gives users full control over security policies, and it's targeted less often by hackers who focus more on online storage.
- Privacy Compliance: Sensitive personal data needs to be stored on-site to meet the requirements of GDPR and other privacy laws.
- Lower Monthly Costs: After the initial purchase price, users don’t have to worry about never ending monthly payment plans for cloud storage.
- Transparent Pricing: Physical storage comes with no hidden costs or surprises.
Disadvantages of Physical Data Storage for Businesses
- High Setup Cost: Purchasing and calibrating the hardware can cost money, especially when large servers are required. Prices have dropped in recent years, but starting costs can be high - particularly for small businesses.
- Requires Technical Knowledge: Physical data storage often requires IT expertise, and this can be an additional long-term cost for businesses.
- Scalability Issues: Increasing physical storage capability requires investing in more hardware.
- Limited Accessibility: Physical storage lacks the global access that cloud storage solutions provide.
As you can see, physical solutions can offer a safe data storage environment. And so despite the growing prevalence of cloud solutions, it still remains a key part of many companies' data storage infrastructure.
Cloud Data Storage Solutions

Cloud storage solutions enable businesses to store data remotely, and access it through their internet connection. It's a viable option for any company and has taken the business world by storm in recent years. In fact, Zippia data estimates that 60% of all US corporate data was stored in one cloud or other in 2023.
Today, businesses have a wide range of different cloud data storage options that are defined by the secure service of tools. Dropbox and Google Drive are probably the most famous ones, but we also recommend IDrive, pCloud, and Internxt.
Advantages of Cloud Storage for Businesses
- Usability and Accessibility: Cloud storage can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, making it great for remote teams. It’s also really easy to use, with intuitive interfaces and drag-and-drop functionality.
- Security: Professional cloud storage solutions normally offer a high level of security that wouldn’t be available to businesses using on-site servers without the expertise.
- Cost-Efficient: Cloud storage is cheap. While they expect monthly payments, businesses don’t have to worry about any large upfront costs.
- Scalable: Businesses only need to pay for the amount of cloud storage they need. And since this approach allows businesses to sidestep physical storage limitations, it’s easy to acquire more storage when required. The reverse is also true, making it a truly flexible option.
- Disaster recovery: Cloud storage limits the fallout from any system failure because all data is stored and backed up somewhere externally. This removes the costs of expensive data retrieval that follow on from physical storage malfunctioning. Cloud providers also automate backup processes.
Disadvantages of Cloud Storage for Business
- Restrictive Control: Since data is stored externally by another company, businesses have limitations around their ability to control and customize the system - an issue of particular importance for big companies.
- Migration Issues: Once businesses have signed up to a particular cloud provider, it can be difficult to migrate to an alternative in the future.
- Internet-Dependence: As offsite storage, cloud solutions require a live connection to access. This means that an internet dropout can drive business to a standstill.
- Contractual Entanglement: It’s common for businesses to be tied into long-term contracts with cloud providers, with obvious risks if the third-party company isn’t meeting expectations.
- Privacy Issues: Cloud storage raises GDPR compliance issues. It necessitates handing over control of confidential information to a third party. This data is tightly controlled by data privacy regulations, with accountability sitting with the first-party business rather than the cloud provider. And if this service transfers data outside of approved geographical boundaries, this can also cause compliance issues.
In sum, cloud solutions can provide secure offsite data storage infrastructure, but with the flexibility, scalability, and professional management that physical alternatives often lack.
Hybrid Data Storage Solutions

As you can see, both physical and cloud data storage solutions have their strengths and weaknesses. Many businesses have decided on a compromise between the two, and this is known as hybrid data storage. These systems use a combination of both cloud technologies and physical, on-premise hardware.
In many ways, this approach to secure data management offers the best of both worlds. It can provide a range of significant benefits for businesses of all sizes, including scalability, agility, and cost saving.
However it also creates its own problems. One comes from simultaneously supervising and monitoring multiple storage systems. Synchronization can be tricky without the right expertise. Another is finding the right people that can manage the distributed infrastructure.
It also brings with it the same risks that come from cloud storage solutions, but special attention needs to be paid to areas such as compliance and data security. This requires understanding which company data requires better protection, storing it in physical storage, and working to ensure that other compliance aspects are respected.
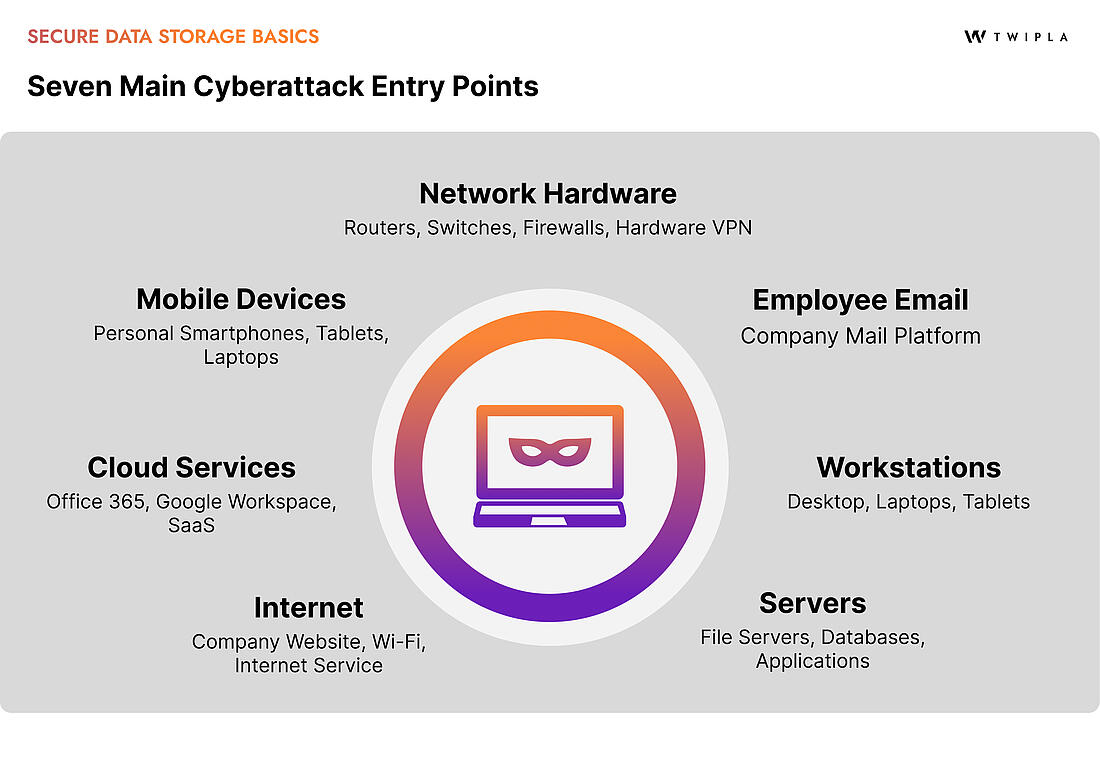
Essential Features of a Secure Data Storage Service
Regardless of whether a business stores data on-site, in the cloud, or using a combination of these technologies, it's important that the system is set up firstly to mitigate the risk of cyberattack. This involves identifying any vulnerable access points to business data, and to then work to lock these doors as much as possible. For organizations with a security operations center (SOC), continuous monitoring of these vulnerabilities can significantly reduce risk.
Then, it's important to look at the underlying characteristics of this infrastructure and related security measures. This can be easier with cloud storage from a respectable provider since their success is built on providing a high level of security. But if businesses want to use on-premise storage, they’ll have to integrate similar elements:
Data Security Policies
Businesses need to implement the right systems and processes around data management. They need to draw up policies that establish appropriate security measures for the different types of data that flow through their organization. This should also include information on the different types of storage devices or cloud solutions used by the organization, and specifying the right measures for each.
Device Security
Businesses need to consider their endpoint security. PCs, smartphones, laptops, and other devices represent potentially vulnerable access doors for cyberattacks, and particularly since the users themselves will not necessarily come through the door with a high level of technical understanding. As such, hardware, software, and related training provide opportunities for maximizing device security wherever possible.
Network Security
When thinking about secure data storage, it’s important to also consider the security of the network that it sits within. Protecting this infrastructure from risk involves implementing such things as firewalls, anti-malware protection, security gateways, and intrusion detection systems. Businesses can also consider incorporating security measures that include both advanced analytics and machine learning. But with the right network security, businesses can prevent the vast majority of attacks from penetrating their system in the first place.
Data Encryption
Encryption is the practice of encoding data in a way that removes sensitive information from being read. It may be stating the obvious, but this is an important part of data security. It works to protect people’s privacy, and secures their information from hackers and other cybersecurity threats. Data should be encrypted both within the storage systems and when it is migrating. Administrators must also implement systems and processes that keep track of any encryption keys.
Data Loss Prevention
Today, many data security experts believe that encryption no longer offers the robust protection against all threats that it once did. Businesses are now urged to also integrate different data loss prevention (DLP) technologies that can identify and protect against any cyber attacks as they happen.
Data Backup and Recovery
Many cyberattacks are so corrosive that the only way to recover any compromised data is to restore it from backups. This means that businesses must ensure that they backup all data regularly, and that this reserve data has the same robust data security in place as their wider data storage system.
Access Controls
Data access controls are the systems that businesses put in place to regulate employee access to any information on file. Threats to data security can come from within an organization as well as outside, and passwords and other access controls will limit these threats significantly. Passwords should be strong and changed regularly, and this access control should also have multi-factor authorization where appropriate.
Data Sensitivity Labels
Sensitivity labels are basically digital stamps that you add to data. Examples include adding a “confidential” label to a sensitive document or email, and this works to encrypt whatever is inside while adding a “Confidential” watermark that highlights its significance.
Secure Deletion
This is the process of permanently erasing sensitive or confidential data. Otherwise known as data erasure or wiping, this ensures that unauthorized people can’t access sensitive or personal information. It’s great for data privacy, it prevents data breaches, and it reduces the opportunities for data theft or other types of data misuse.
TWIPLA and Secure Data Storage
Here at TWIPLA, we're privacy advocates - a principle that naturally extends to our data storage infrastructure. Our data centers are characterized by the highest level of data security available today, with cutting edge encryption and firewalls that protect users from breaches and other threats to data.
This data storage is also audited on a regular basis by authorities and holds ISO 27001 certification, which is recognition that it has the highest data security standards found anywhere in the world.
What’s more, our data centers are located in Germany, a location that takes data security seriously. It’s a deliberate move that ensures our compliance with data protection regulations and gives our users further assurances about the security of their website data.
Data Minimization
We're also big fans of data minimization. This means that we limit the collection, storage, and retention of data to what we need to achieve our goals. It's a key element of our data privacy strategy, and protects our users - and their website visitors - from harm.
One of the more obvious aspects of this can be understood with how our website intelligence platform collects data. In default Maximum Privacy Mode, data capture is limited to approximate visitor technical specifications rather than any personal data. In this mode, it complies with all global privacy requirements, while also providing businesses with the insights they need to guide online success.
But TWIPLA has three lower data privacy levels. These collect more data on visitors, but are still designed with the principles of data minimization in mind. And if users need these different volumes of visitor data for their business, our Privacy Center and wider Resource Library provides all the help they need to stay legally compliant.
That’s Secure Data Storage Explained
And that’s it, that’s what you need to know about data storage. It’s another area that businesses need to get right, but getting your head around which of the different secure, encrypted data storage solutions fits best will lay the groundwork for future success.
If you found this blog useful and want a summary about everything we publish, then subscribe to our monthly newsletter. You’ll receive a single email on the last Thursday of each month, with links to all our new content as well as details of any upcoming events and updates to our website intelligence platform.
Share article
Get Started for Free
Gain World-Class Insights & Offer Innovative Privacy & Security