- Why Us?
- Features
White Label
For SaaS Platforms & Agencies
Provide our complete analytics suite to your clients, directly within your own interface and with your/their own branding. Discover Analytics-as-a-Service and White Label Analytics. Great benefit, minimal effort.
- Pricing
- White Label
- Blog
- Chatbots, Assistants & AI Search: Tracking AI-Driven Website Traffic
- Use Case: Using TWIPLA’s Conversion Funnels to Uncover Onboarding Friction
- Website Intelligence News Roundup February 2025
- Website Intelligence News Roundup January 2025
- Alarming Behavior Tracking: Dead Clicks, Rage Clicks and More
- Data Management Strategy: Steps + Insights from Aleksejs Plotnikovs
- Craft a Successful Data Analytics Strategy in 6 Steps
- Interview: Aaron Weller on AI Privacy Challenges
- ResourcesExpand Your KnowledgeGetting Started
What is Data Privacy? Your Data, Your Rules, Your Future

Did you know that 81% of internet users think that how a company handles their data shows how much they’re valued as a customer?
That’s one of the more striking findings from Cisco’s Consumer Privacy Survey, and it underlines just how important this issue is for clients and consumers.
But what is data privacy actually? Unfortunately, many businesses don’t fully understand what the term refers to. It’s also often confused with “data security" or under-prioritized even though good practices here will actually increase sales and drive down ROI.
If you’re looking to understand exactly what data privacy is, then this blog is a great place to start. Read on and you’ll learn about data privacy, where it sits in the three pillars of data protection, and the software that makes compliance just a little bit easier for businesses.
So, What is Data Privacy?
→ Your Unseen Digital Bodyguard
Data privacy is what empowers individuals with control over their personal information.
It’s as simple as that, giving people agency over their identity in the digitized world.
It’s also a fundamental human right.
For reference, here’s Article 12 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights:
No one shall be subjected to arbitrary interference with his privacy, family, home or correspondence, nor to attacks upon his honour and reputation. Everyone has the right to the protection of the law against such interference or attacks.
So, what is data privacy but something that’s as important as the right to be:
- Free from torture
- Equal under the law
- Free from slavery
- Presumed innocent until found guilty
- Free to express themselves
Data privacy is also one of the United Nations Human Rights Council resolutions, and is reinforced by the hundreds of privacy laws that have emerged globally over the last decade.
And that’s because of the harm people can suffer if their data gets into the wrong hands.
Given this, data privacy is the digital bodyguard that protects people online.
All in all, it’s a pretty big deal, even if there are many who argue that a lot has gone wrong with internet user data rights.
But of course, we all have responsibilities ourselves. People should protect their rights by reading up on the subject of privacy. They can also pay attention to the settings of their:
- Devices,
- Browsers,
- Apps, and
- Accounts.
They can also be proactive about many of their rights to privacy - and particularly the right to access, edit, or delete whatever information that businesses hold about them.
But here’s the kicker:
Privacy laws exist to protect people from having their personal information exploited by businesses.
So businesses take note, these laws are there to control you. It means that organizations need to handle personal data:
Responsibly.
Transparently.
And securely!
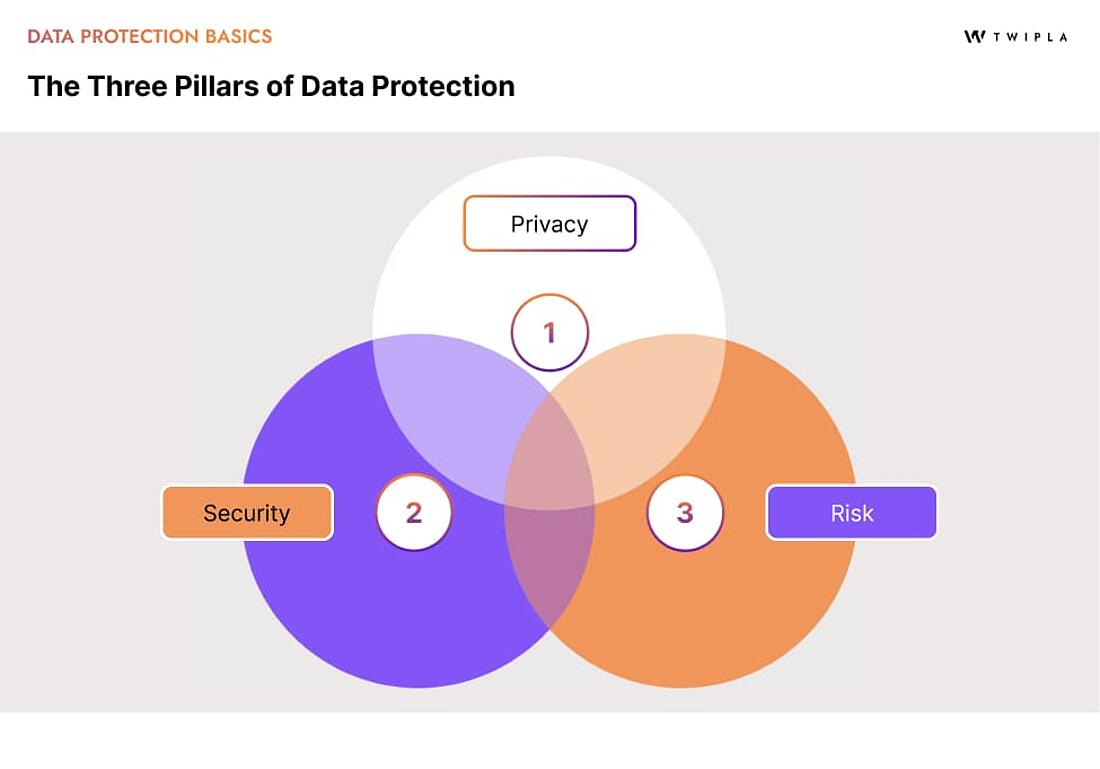
Data Privacy vs Data Security
These are two main pillars of data protection.
There’s actually three focus areas when you include risk assessment (but more on that later).
People often confuse privacy and security, and it’s easy to see why - there’s real overlap between the two.
So what is the difference between data security and data privacy?
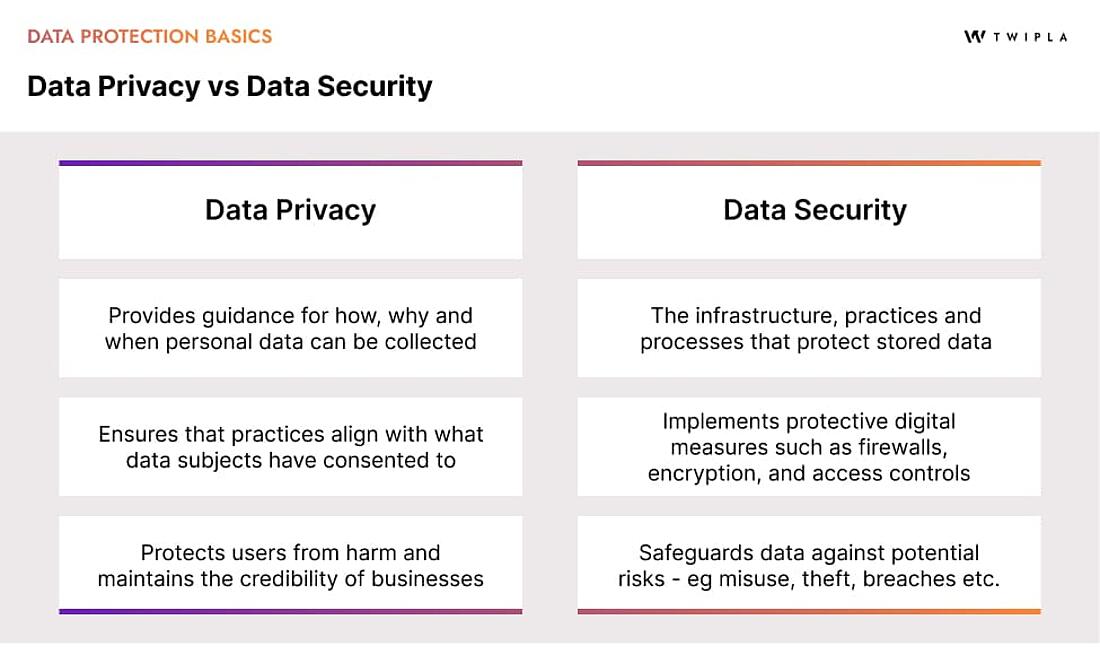
-> Data privacy means managing data in line with data subject rights.
-> Security means protecting data from unauthorized access, breaches, and other threats.
But what is a breach in data privacy you ask?
Simply put, it’s the unauthorized access, disclosure, or loss of personal or sensitive information that compromises the confidentiality and security of that data.
Maybe this information will end up in the hands of your competitors, at home with an employee, or even on the dark web. In any case, you’re breaking the law.
Privacy requires security and security requires privacy.
For instance, encryption and access controls are essential for maintaining data security since these things safeguard data from potential breaches. Conversely, strong privacy practices ensure that data security measures are applied appropriately and that personal data is not exposed in ways that violate privacy rights.
Ultimately, these two pillars work together to create a framework for protecting personal information; let's recap:
Data Protection and Risk Management
So, on to the third and final pillar of data protection.
Risk management covers all the work needed to systematically identify, assess, and minimize the risks involved when handling personal data.
So while privacy and security address how data is managed and protected, risk management is the third eye 👀 that allows businesses to search for and then address potential threats and vulnerabilities in their infrastructure.
These risks could be anything from data breaches and system failures to non-compliance with regulations.
But by being proactive about risk management, businesses put themselves in a good position to prevent or minimize the impact of these dangers.
That’s 70% of the world with data privacy laws in place. So for the moment there’s 30% of the global population that might not know what is data privacy, but they soon will once the remaining countries get their acts together and finish drafting their own legislation.
This legislation represents “No Trespassing” signs that are hammered deep into personal data, and we’ve got a whole section of our website dedicated to these global privacy laws.
In effect, they establish clear guidelines on how customer data can be collected, used, stored, and shared.
Privacy Laws give people the power to hold businesses accountable when they fall short of their legal obligations.
For instance, the European Union’s GDPR and California’s CCPA give their respective citizens the right to know what information is being collected on them, who has access to this data, and the reasons why businesses need it in the first place.
And if obligations aren’t met, these laws also empower individuals to take action, something that they can do by filing complaints, seeking compensation, or demanding the correction or deletion of their information.
The Data Privacy Framework
If somebody asks you what is data privacy and why is it important, you can probably explain it to them better than you could before reading this blog.
But you likely now want to know how your business can meet compliance requirements.
There's certainly work to do so that you company is meeting your legal responsibilities, particularly when it comes to marketing compliance. These include:
- Securing your data storage infrastructure
- Minimizing the amount of data you hold on customers
- Anonymizing any personal data on file
- Creating a watertight privacy policy
In practice, the best way is to develop what is known as a data privacy framework.
But what is a data privacy framework?
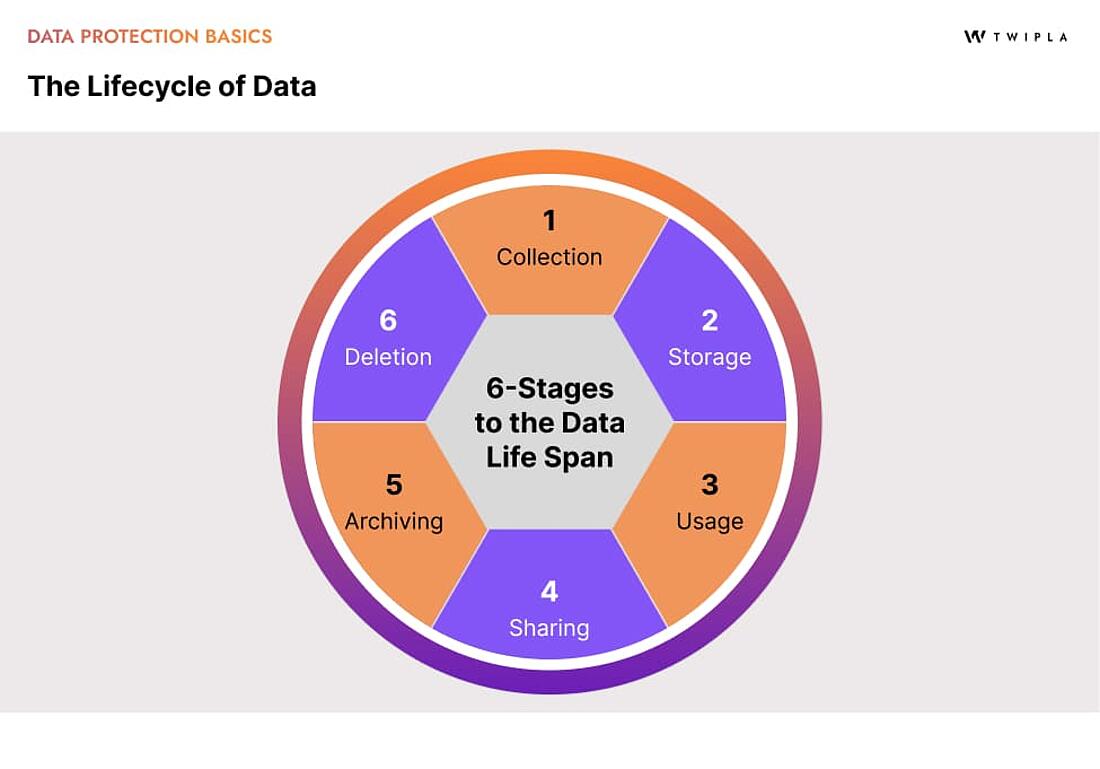
A Data Privacy Framework is a structured approach to data protection that enables companies to manage and protect personal data throughout its full lifecycle.
For reference, here's what the full data lifecycle looks like for businesses:
When data protection is considered at each stage of the data lifecycle, it ensures that information is handled in compliance with all legal, ethical, and organizational standards.
And in practice, this encompasses the processes and practices that will safeguard the privacy of individuals and ensures that their personal data is managed with the care and respect that it deserves.
Data Privacy Challenges
→ Conflict Between Users and Businesses
Now, it’s important to note that data privacy creates some friction between businesses and internet users.
-> Businesses see data as the lifebood of digital success, with many feeling that more data therefore means better results.
-> Customers are highly aware of the dangers posed by the internet to their personal information, and want to control who has access to it (and how much).
Businesses and internet users also have very different levels of understanding when it comes to what is a data privacy policy, data collection practices, and compliance responsibilities:
Challenge | User | Business |
Lack of awareness about privacy risks | Yes | Yes |
Difficulty understanding privacy policies | Yes | Sometimes |
Limited control over data collection practices | Not anymore | No |
Complexity of data privacy laws | No | Sometimes |
High cost of Implementing privacy measures | No | Not anymore |
However, times are changing:
-> Users now have more control over data collection practices.
-> Businesses don’t have to worry about the high cost of privacy measures anymore, and understanding privacy policies and data privacy laws is also easier than ever.
Privacy is now easier to achieve for everyone thanks to privacy-first technologies.
Introducing Privacy-First Tech
New laws often stimulate innovation, something that has been shown to be true during the current age of data privacy.
From cookieless analytics to privacy-respecting website builders, consent management platforms, and chatbots, businesses have the tech at their fingertips that can remove their privacy compliance burden completely.
What’s more, enhancing data privacy is a great way for companies to increase their ESG ratings, and open themselves up to more investment opportunities.
But it’s also a social good that will increase trust, and with customer loyalty and sales!
TWIPLA and Data Privacy
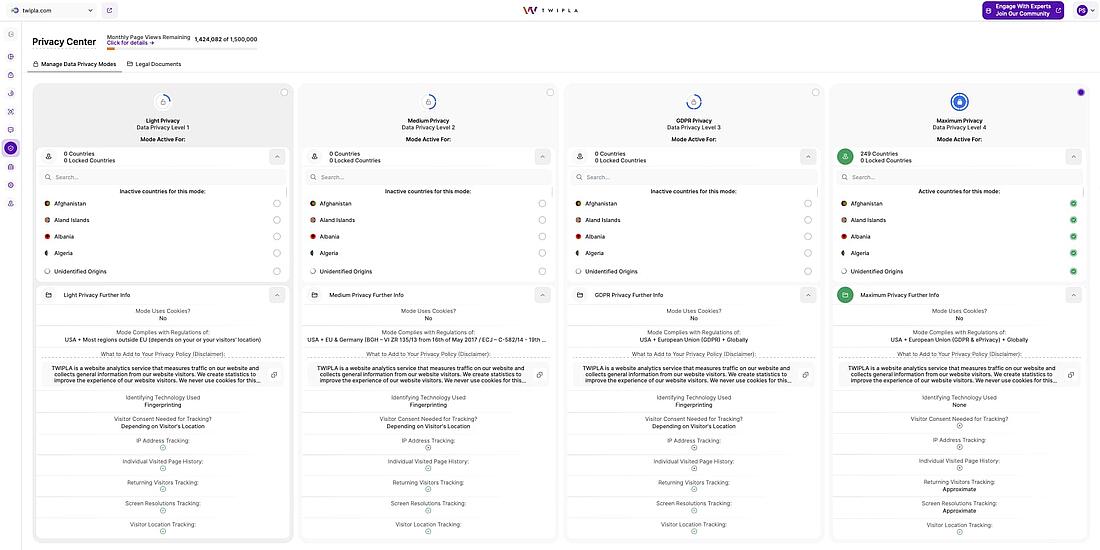
Here at TWIPLA, we’re privacy advocates and our website intelligence platform meets any legal threshold that exists globally.
In default Maximum Privacy Mode, it meets all global requirements - including GDPR and ePrivacy. This allows clients to leverage analytics without needing a cookie banner.
However, clients can also activate one of three lower-threshold privacy levels, or can set TWIPLA to a different privacy mode for any visitor country of origin.
And when set in any of these lower privacy modes, it can also be calibrated to collect a legitimate data fundmament on website visitors that reject the cookie banner - meaning that businesses have the option to collect insights on EVERY customer.
That's Data Privacy Explained
And that's it, that's your introduction to the world of data privacy.
It's a fascinating subject, and one that will only increase in importance as data privacy laws develop and enforcement agencies become more effective.
If you found this blog useful, then feel free to share it around! And if you want to stay up-to-date with everything we publish, the best way is to sign up to our newsletter.
That way, you'll receive one email at the end of each month with a summary of all our new resources, as well as updates about our website intelligence platform.
Share article
Get Started for Free
Gain World-Class Insights & Offer Innovative Privacy & Security